Are you a gardening enthusiast who is always looking for new ways to care for your plants? Have you considered switching to hydroculture, a soil-less plant cultivation method that can yield incredible results? As someone who loves sharing tips and ideas on how to care for plants, I am excited to discuss the benefits of hydroculture and the different methods used in hydroponics. In this article, we will explore why you should consider switching to hydroculture, how it works, and the different types of hydroponic systems, including the popular passive hydroponic systems.
So, if you’re looking for a way to take your gardening to the next level, keep reading!
Why Choose Soil-less Plant Cultivation: Hydroculture vs. Hydroponics
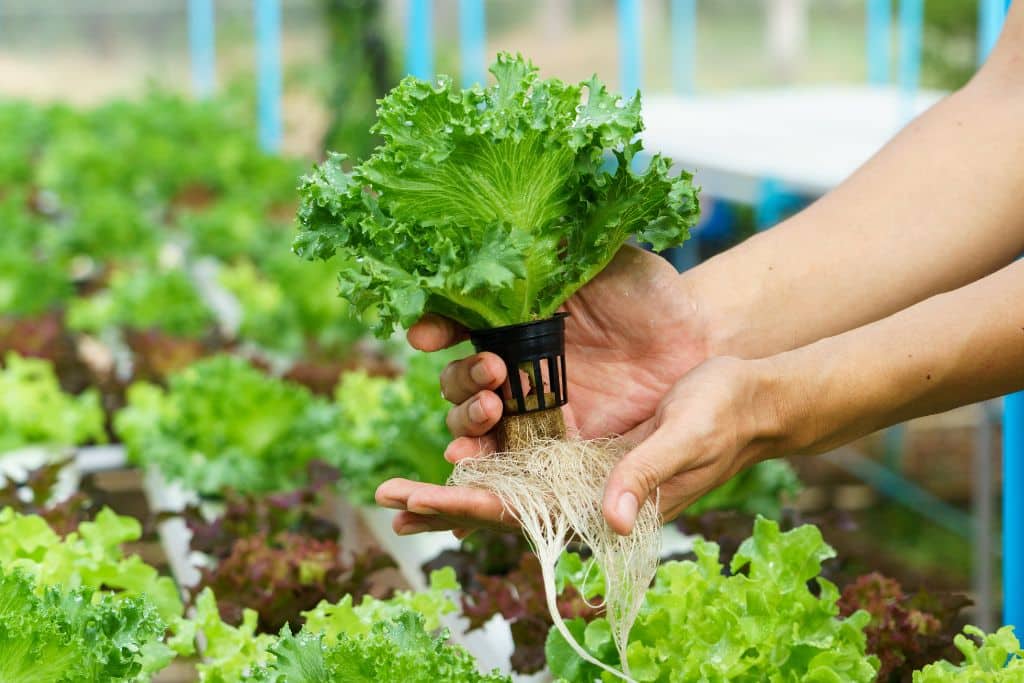
Hydroculture and hydroponics are two methods of cultivating plants without organic substrates. In hydroponics, the plant roots are immersed entirely in a nutrient solution. Hydroculture, on the other hand, utilizes a substrate for growing plants while delivering nutrient solution directly to the roots.
Although the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, there are subtle differences between the two. The major distinction lies in the use of a substrate in hydroculture, which supports the roots and helps with moisture retention. In hydroponics, the roots hang freely in the nutrient solution.
Despite these differences, both methods have advantages over traditional soil-based gardening. Hydroculture, for example, reduces the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests, while hydroponics uses less water and requires less space. Additionally, both methods allow for precise control over nutrient delivery, resulting in healthier and faster-growing plants.
In the following article, we will discuss the benefits of hydroculture in greater detail and compare them with those of hydroponics. Whether you’re an experienced gardener or just starting out, you won’t want to miss this informative guide on the advantages of soil-less cultivation.
Hydroculture Benefits: Why You Should Consider Switching to Soil-less Plant Cultivation
If you’re looking for a more efficient and effective way to grow plants, hydroculture might just be the answer. Here are some of the key benefits of this soil-less cultivation method:
- No risk of root-damaging pests or diseases
- No need for watering plants manually
- Efficient use of space
- Reduced water loss through condensation
- Faster and more abundant growth, depending on the plant
- No weed growth
Given these advantages, it’s no wonder that more and more gardeners are switching to hydroculture. In the next section, we’ll explore the reasons why you should consider making the switch as well.
Why You Should Switch to Hydroculture?
If you’re looking for a way to cultivate plants more efficiently and with less hassle, hydroculture might be the perfect solution. Here are some reasons why you should consider making the switch:
- Indoor crops can be grown all year round
- Less logistical effort as no soil is required, which also means no insects attracted to the soil
- Efficient use of space and higher yields with vertical farming
- Easy maintenance for ornamental plants as the water level provides a clear indication of when to water
Given these benefits, it’s worth considering hydroculture as an alternative to traditional soil-based cultivation methods. In the next section, we’ll delve into how hydroculture actually works.

How does Hydroculture Work?
To grow plants hydroponically, there are three essential elements that must be provided:
- Light and the appropriate temperature
- Water
- Air and nutrients
Compared to traditional cultivation methods, the way plants receive light remains the same (except for artificially lit plants). The difference lies in how plants receive their water and nutrients. A plant grown in soil must be watered regularly to absorb water while simultaneously taking up nutrients from the soil.
In hydroculture, plants are grown without soil, and instead, their roots are immersed in a nutrient-rich water solution. The water solution provides the plants with essential minerals and nutrients, while an air pump ensures that the roots have enough oxygen. The result is faster growth and a more efficient use of resources. In the next section, we’ll explore the different types of hydroculture systems available.
Different Methods in Hydroponics – Active and Passive Systems
Hydroponics involves growing plants without soil by using water-based nutrient solutions. There are two main types of hydroponic systems: active and passive.
Active Hydroponic Systems
Active hydroponic systems require electricity and the use of various instruments and tools such as oxygen pumps and lighting systems. However, they offer the ability to grow all types of plants that grow above ground and produce fruits.
Deep Water Culture (DWC)
The DWC system involves growing plants with their roots fully submerged in a nutrient solution. To prevent drowning of the plant, an air stone is used to oxygenate the water.
Ebb & Flow
The Ebb and Flow system, also known as flood and drain, is similar to the DWC system. However, in this system, the plant roots are not always submerged in water. The nutrient solution is pumped into the plant reservoir at regular intervals, submerging the roots, and then drained back into the reservoir.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
In the NFT system, the plants are placed on a slanted rail or tube. The nutrient solution is pumped into the top of the rail, and gravity helps to flow the solution down the rail, providing the plants with water, nutrients, and air.
Drip System
The drip system is a popular active hydroponic system that involves a pump and a series of tubes that deliver nutrient solution to the plants’ roots. The nutrient solution is dripped onto the plants’ growing medium or roots, providing them with water and nutrients.
Aeroponic System
The aeroponic system involves suspending the plants’ roots in the air and misting them with a nutrient solution. This system uses less water compared to other hydroponic systems and is ideal for growing plants that require a lot of oxygen, such as lettuce and herbs.
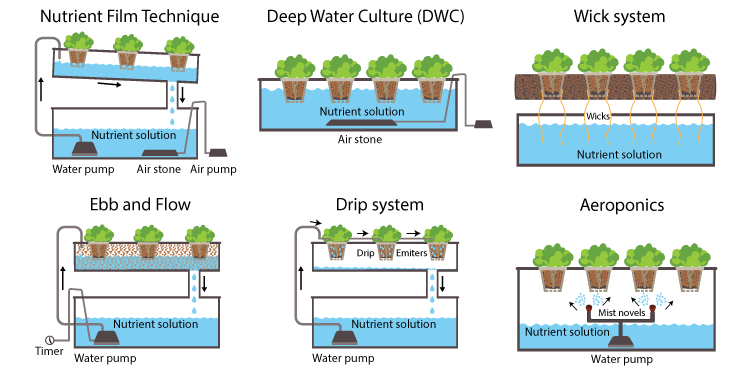
Passive Hydroponic System
Passive hydroponic systems do not require electricity and are often simpler in design compared to active systems. However, they are limited to growing plants that do not require much water or nutrients.
Wick System
The wick system is one of the simplest passive hydroponic systems. It involves placing a wick (usually made of cotton) into a container of nutrient solution and then into the plant’s growing medium. The wick slowly draws the nutrient solution into the growing medium, providing the plants with water and nutrients.
Water Culture (Static Solution Culture)
The water culture system involves suspending the plants’ roots in a nutrient solution. The plants are usually placed in a net pot or a foam raft, with their roots dangling in the nutrient solution. An air stone is used to oxygenate the water and provide the plants with the necessary air.
Main differences between active and passive systems
The main difference between active and passive systems is that no electronic devices are used in passive systems. These systems are often used for decorative plants. Passive systems can be divided into substrate-based and substrate-free systems.
In substrate-free systems, the plants are placed in a reservoir with nutrient solution, which is drawn up through capillary action without external influence.
In substrate-based methods, the plants are placed in a container with porous materials such as pumice, coconut fibers, or other sufficiently capillary-active substances. Then, a reservoir beneath the substrate is filled with nutrient solution. Through the porosity of the substrate and the capillary action of the roots, water is drawn to the plant. A small water level indicator helps to estimate when the reservoir needs to be refilled.
When using passive hydroponic systems, it is important to regularly check the pH level of the nutrient solution, as well as the water level in the reservoir. In addition, the plants should be regularly checked for pests and diseases, as they can spread quickly in hydroponic systems.
Proper lighting and temperature control are also important for the growth and development of plants in passive hydroponic systems. Finally, the nutrient solution should be changed regularly to prevent the buildup of excess salts and other nutrients, which can harm the plants.
Things to consider when using passive hydroponic systems
- The water level and container should be checked once or twice a week, and only filled to the optimal level.
- When the water level is low, wait 2 days for plants in sunny locations and 5 days for plants in shady locations before adding more water. Plants are often over-watered, rather than drying out.
- Using the right fertilizer is crucial. Ion exchange fertilizers are usually effective because their granules contain resin, whose ions react with the calcium and magnesium in the water.
- Almost all plants are suitable for hydroponics, but there are exceptions. Long-lived green plants are preferred over short-lived flowering plants, as the system is designed for longevity. Plants that cannot tolerate waterlogged soil, such as orchids or cacti, are not suitable for hydroponics.
If you want to learn more about hydroponics and hydroculture, watch a time-lapse of hydroponic growth, or explore these book: Hydroponic Basics.
Final Thoughts
As a gardening enthusiast, I hope this article has helped you understand the basics of hydroponics and its benefits for growing plants. Whether you’re looking to start a garden indoors or outdoors, hydroponics can be a great option. By using water and nutrients instead of soil, you can grow plants faster and with less effort. Remember to choose the right system, monitor water levels, use the appropriate fertilizer, and select plants that are suitable for hydroponics. With these tips, you can start your own hydroponic garden and enjoy the rewards of fresh and healthy plants.
If you’re interested in exploring more about hydroponic gardening, be sure to check out our article on the Legendary Kratky Method – Growing Plants Without Soil & Without Watering.




7 comments