Aeroponics and fogponics are two modern farming techniques that have gained popularity over the years. Both methods involve growing plants without the use of soil, but they differ in the way they deliver nutrients and water to the plant roots. In aeroponics, plants are grown in a closed environment where nutrient-rich water is misted onto the roots. On the other hand, fogponics is a modified version of aeroponics that uses a fog-like mist to deliver nutrients to the roots.
Key Takeaways
- Aeroponics and fogponics are two indoor and modern farming techniques that involve growing plants without soil.
- The main difference between aeroponics and fogponics is how they deliver nutrients and water to the plant roots.
- Understanding the differences between aeroponics and fogponics can help growers choose the best method for their needs.
- Fogponics is believed to be more efficient than aeroponics as it allows for better nutrient absorption and can reduce water usage.
Understanding Aeroponics
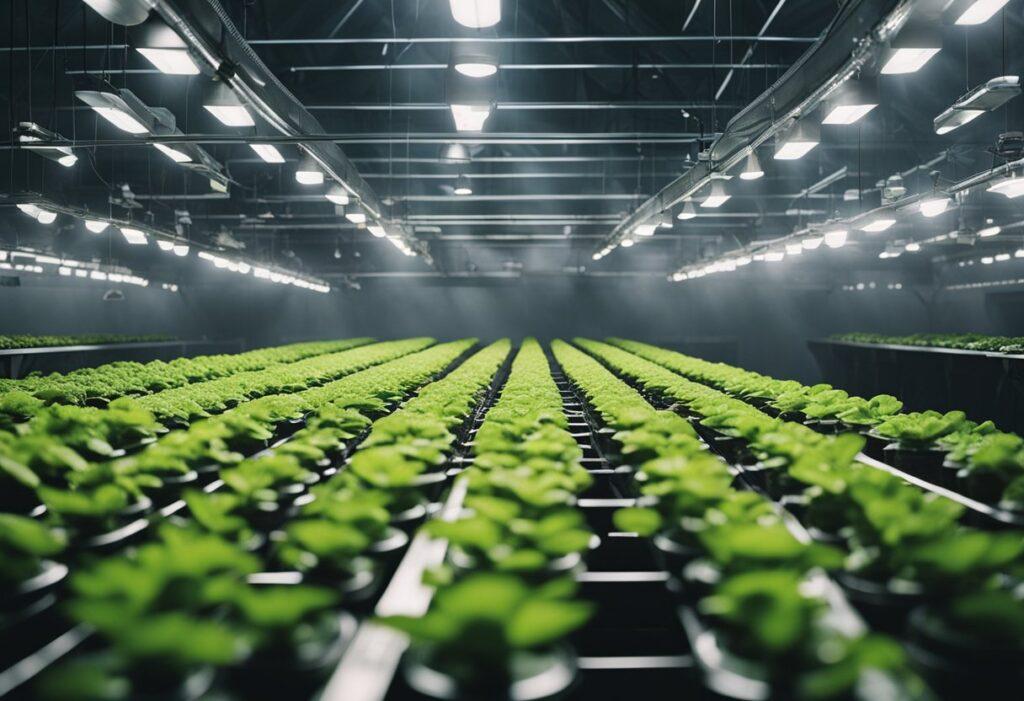

Basic Principle of Aeroponics
Aeroponics is a soilless cultivation technique that involves growing plants in an environment where their roots are suspended in the air and sprayed with a nutrient-rich mist. The basic principle of aeroponics is to provide plants with a highly oxygenated environment that promotes rapid growth and development.
In an aeroponic system, the plant roots are suspended in a chamber or container, and nutrient-rich water is sprayed onto the roots in a fine mist. High-pressure pumps or ultrasonic foggers typically generate the mist. The roots absorb the nutrients directly from the mist, and the excess water drains away.
If you’re interested in learning more about Ultrasonic Hydroponic Fogger check out this article that discusses hydroponics and the use of ultrasonic foggers in more detail.
Advantages of Aeroponics
Aeroponics has several advantages over traditional soil-based cultivation methods. One of the main advantages is that it allows for more efficient use of resources such as water and nutrients. Since the roots are suspended in the air, they have access to more oxygen, which promotes faster growth and higher yields. Additionally, since the roots are not in contact with soil, the risk of soil-borne diseases is greatly reduced.
Another advantage of aeroponics is that it allows for greater control over the growing environment. The nutrient solution can be precisely controlled and adjusted to meet the plants’ specific needs, and the environment can be optimized for maximum growth and yield.
Limitations of Aeroponics
Despite its many advantages, aeroponics also has some limitations. One of the main limitations is that it requires a certain level of technical understanding and expertise to set up and maintain. The system must be carefully designed and calibrated to ensure that the plants receive the proper amount of nutrients and water. Additionally, aeroponic systems can be more expensive to set up and maintain than traditional soil-based systems.
Another limitation of aeroponics is that it can be more susceptible to power outages or equipment failures. Since the plants rely on a constant supply of nutrient-rich mist, any interruption in the system can have a detrimental effect on growth and yield.
Understanding Fogponics
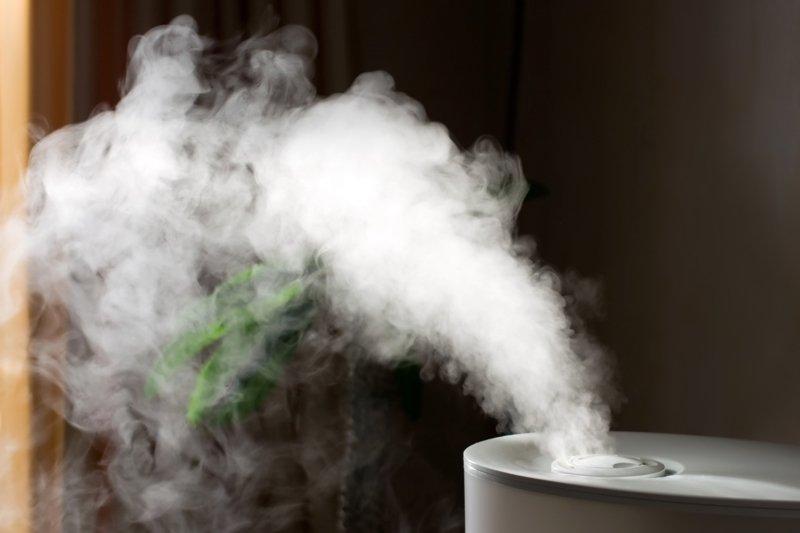

Basic Principle of Fogponics
Fogponics is a type of hydroponic system that uses a fine mist to deliver nutrients to plants. The basic principle of fogponics is similar to that of aeroponics, but instead of using a high-pressure mist, fogponics uses a low-pressure mist. The nutrient solution is delivered to the roots of the plants in the form of a fine mist, which is absorbed by the plants.
Advantages of Fogponics
Fogponics has several advantages over traditional hydroponic systems. First, it is more energy-efficient than other hydroponic systems because it requires less water and nutrients. Second, it is easier to maintain than other hydroponic systems because it does not require frequent nutrient changes. Third, it is less prone to disease and pest problems because the fine mist creates a more humid environment that discourages pests and diseases.
Ultrasonic hydroponic foggers, like the Ultrasonic Mist Maker 12 Head Ultrasonic Pond Fogger 400W Humidifier Fog Machine, represent an innovative way of providing moisture to plants grown in hydroponic systems. These devices use ultrasonic vibrations to create a fine mist of water droplets that can be absorbed by plant roots. The key components of an ultrasonic hydroponic fogger include the ultrasonic module, water reservoir, and fog nozzle.

Limitations of Fogponics
Despite its advantages, fogponics also has some limitations. First, it can be more expensive to set up than other hydroponic systems because it requires specialized equipment. Second, it may not be suitable for all types of plants because some plants may not be able to absorb nutrients from a fine mist. Finally, it may require more frequent monitoring than other hydroponic systems because the mist can clog or become contaminated with bacteria or other microorganisms.
Key Differences Between Aeroponics and Fogponics
Method of Nutrient Delivery
The main difference between aeroponics and fogponics is in the method of nutrient delivery. In aeroponics, the roots of the plants are suspended in the air and sprayed with a nutrient-rich mist. The mist is made up of droplets that are typically around 50 microns in size. This allows the roots to absorb the nutrients they need while also receiving plenty of oxygen.
On the other hand, fogponics uses an even finer mist to deliver nutrients to the roots of the plants. The mist is so fine that it resembles fog, hence the name. The droplets in a fogponics system are typically less than 10 microns in size. This allows the nutrients to be absorbed more quickly and efficiently by the roots.
Efficiency
Due to the smaller droplet size used in fogponics, this method of nutrient delivery is generally considered to be more efficient than aeroponics. The smaller droplets allow for faster absorption of nutrients, which can lead to faster growth rates and higher yields.
However, it is worth noting that fogponics systems can be more complex and expensive to set up than aeroponics systems. This can make them less accessible to some growers.
Cost and Maintenance
In terms of cost and maintenance, aeroponics systems are generally considered to be more affordable and easier to maintain than fogponics systems. Aeroponics systems are simpler in design and require fewer components, which can make them a more attractive option for growers who are just starting out or who have limited resources.
Fogponics systems, on the other hand, require more specialized equipment and may require more frequent maintenance to ensure that the mist is being delivered properly to the plants.
Applications and Uses
Both aeroponics and fogponics are highly efficient and innovative methods of growing plants without soil. They are used in a variety of applications, ranging from small-scale indoor gardening to large-scale commercial farming.
Aeroponics Applications
Aeroponics is commonly used in research facilities and laboratories for plant propagation and experimentation. It is also used in space exploration programs to grow plants in microgravity conditions. Aeroponics is also utilized in commercial farming for growing high-value crops such as lettuce, herbs, and strawberries.
Fogponics Applications
Fogponics is a relatively new technology that is gaining popularity in indoor gardening and small-scale farming. It is used to grow a wide range of plants, including vegetables, herbs, and flowers. Fogponics is ideal for small spaces, as it does not require large amounts of water or space. It is also used in research facilities and laboratories for plant propagation and experimentation.
Both aeroponics and fogponics are highly efficient and innovative methods of growing plants without soil. They are used in a variety of applications, ranging from small-scale indoor gardening to large-scale commercial farming.
Conclusion
Both aeroponics and fogponics are advanced methods of soilless farming that use mist or fog to deliver nutrients to plant roots. Although they share similarities, there are some differences between the two.
Aeroponics is a system that uses a high-pressure mist to deliver nutrients to the roots of plants, while fogponics uses a low-pressure mist to deliver nutrients. Aeroponics is more efficient in terms of water usage and nutrient delivery, but it requires a higher initial investment. Fogponics, on the other hand, is less expensive to set up and maintain, but it may not be as effective in delivering nutrients to the plants.
Both systems have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between the two depends on various factors such as the type of plants being grown, the available resources, and the goals of the farmer. It is important to carefully consider these factors before deciding which system to use.




1 comment